 Esperanto
Esperanto
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
 Euskara
Euskara
 Zulu
Zulu
 Latinus
Latinus
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
 Slovak
Slovak
 Slovak
Slovak
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
19
2025
-
09
LinkedGo Air to Water Heat Pump: Primary/Secondary System Application
author:
LinkedGo Air to Water Heat Pump: Primary System Application
The primary system is the heat-generation side of a hydronic network.
When paired with a LinkedGo air to water heat pump, it becomes the powerhouse that produces, stabilizes, and stores hot water before it’s distributed throughout the building.
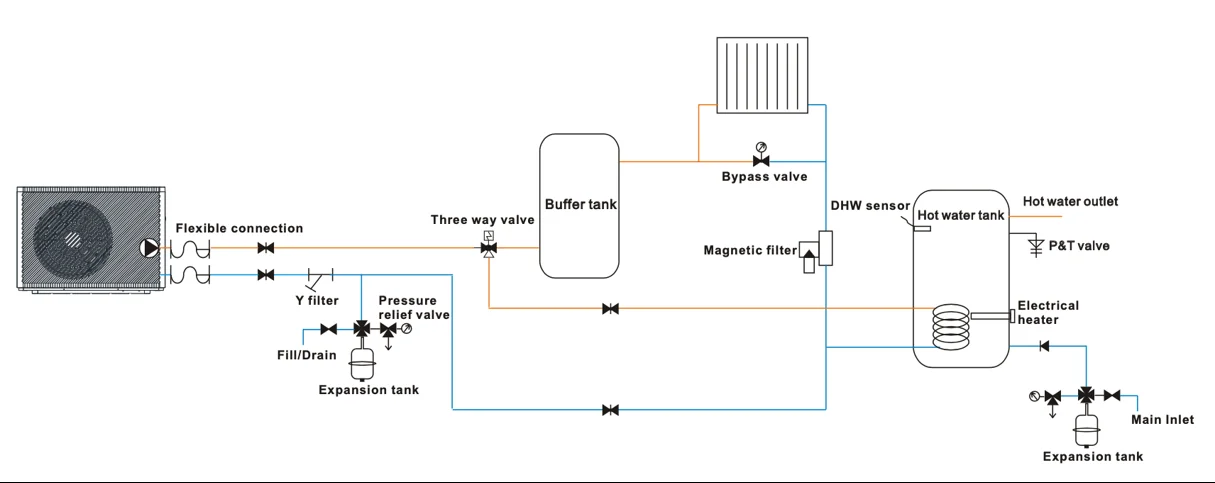
Key Components and Their Roles
LinkedGo Air to Water Heat Pump – Extracts renewable energy from outdoor air and raises water temperature for heating and domestic hot water (DHW).
Flexible Connection – Flexible hoses reduce vibration from the pump and simplify installation.
Y-Filter – Captures dirt and sludge, protecting pumps, valves, and the heat pump’s heat exchanger.
Pressure-Relief Valve – Opens if system pressure rises dangerously high, preventing damage.
Fill/Drain Valve – Allows the system to be filled with water or drained for maintenance.
Expansion Tank – Absorbs the natural volume change of heated water, keeping pressure stable.
Three-Way Valve & Controls – Directs hot water toward the buffer tank for space heating or to the indirect coil inside the domestic hot-water cylinder.
Buffer Sensor – Measures water temperature in the buffer tank and signals the controls when the heat pump should run.
How It Works
The LinkedGo heat pump circulates warm water through the primary loop.
The three-way valve, guided by buffer and DHW sensors, decides whether that heat goes to:
The buffer tank for space heating, or
The indirect coil inside the hot-water cylinder for taps and showers.
Because the primary loop is dedicated to generation only, flow and temperature remain stable, which protects the compressor and maximizes seasonal efficiency.
Best-Fit Applications
Single-zone residences that need constant water temperature.
Central mechanical plants for multi-unit buildings.
Facilities with high domestic hot-water demand, such as boutique hotels or gyms.
LinkedGo Air to Water Heat Pump: Secondary System Application
The secondary system is the distribution and storage side of the hydronic network.
It draws heat from the buffer tank and delivers it to the spaces and fixtures that need it.
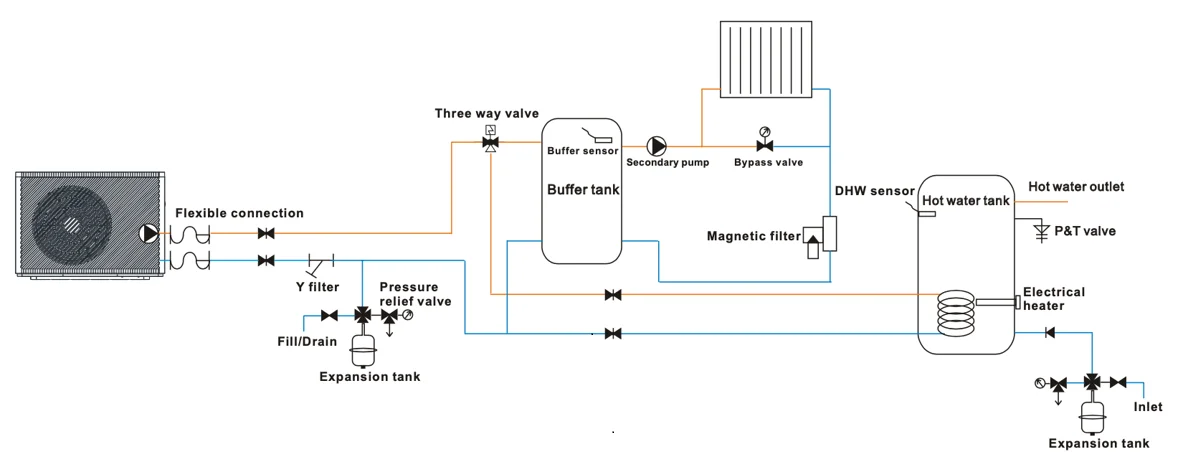
Key Components and Their Roles
Secondary Pump – Circulates hot water through radiators, fan-coil units, or radiant-floor circuits without disturbing the primary loop.
Bypass Valve – Maintains minimum flow through the pump if all zone valves close, preventing noise and pump damage.
Buffer Tank – A thermal “battery” that de-couples generation from distribution and prevents short-cycling of the heat pump.
Magnetic Filter – Captures iron-oxide sludge and keeps system water clean.
Indirect Domestic-Hot-Water (DHW) Tank – Holds potable water heated by a coil fed from the primary loop.
DHW Sensor – Measures hot-water temperature to guarantee a reliable supply for showers and sinks.
Hot-Water Outlet – Delivers heated potable water to taps and fixtures.
Pressure & Temperature (P&T) Valve – A critical safety device that relieves pressure or temperature spikes.
Immersion Heater – An electric element for backup or for heating water during off-peak electricity rates.
Main Inlet – Cold-water supply that feeds the hot-water cylinder.
How It Works
Hot water from the buffer tank enters the secondary circuit.
Zone pumps or valves modulate flow to each radiator, fan coil, or under-floor loop based on room thermostats.
When the DHW tank calls for heat, the secondary loop can also divert energy to the indirect coil, ensuring a steady supply of domestic hot water.
Because this loop is hydraulically independent, adjusting zone temperatures does not disturb the heat pump’s operation—ideal for multi-zone homes or offices.
Best-Fit Applications
Multi-zone residences requiring different temperatures for bedrooms, living areas, and bathrooms.
Light-commercial properties such as offices or clinics with separate comfort zones.
Retrofit projects where radiators, fan-coil units, and radiant floors coexist.
Why LinkedGo Air to Water Heat Pumps Excel in Both
High Seasonal Efficiency (COP) – Inverter technology maintains output even in cold climates.
Quiet, Reliable Operation – Perfect for residential neighborhoods or mixed-use buildings.
Smart Controls & Self-Diagnostics – Simplify integration with primary and secondary loops.
Eco-Friendly Refrigerant – Meets EU and North-American sustainability targets.
related news
undefined







